Diabetic Foot Cure and Diabetes Treatment in Cuba for Foreigners
 Diabetes can be managed effectively and controlled once it has been accurately diagnosed. The goal of diabetes management is to prevent short-and long-term complications of diabetes from developing.
Diabetes can be managed effectively and controlled once it has been accurately diagnosed. The goal of diabetes management is to prevent short-and long-term complications of diabetes from developing.
Without proper management, people with diabetes can develop serious or deadly complications from high glucose levels, including blindness, kidney disease and nerve damage, as well as vascular disease that can lead to amputations, heart disease, and strokes. Uncontrolled diabetes can complicate pregnancy; birth defects are also more common in babies born to women with uncontrolled diabetes. Treating diabetes in a comprehensive manner includes not only managing blood glucose but also blood pressure and cholesterol. This is crucial in helping to prevent heart attacks and stroke.
There is good news; people with diabetes who maintain lower blood glucose, blood pressure and cholesterol levels can lower their risk of cardiovascular disease. Diabetes treatment guidelines emphasize the importance of aggressive blood pressure control in lowering the risk for heart disease, stroke, and early death in people with diabetes. Before most of the focus in diabetes care had been on tightly controlling blood sugar, but new evidence suggests that both blood sugar and blood pressure are very important in managing the disease.
WHAT IS DIABETIC FOOT?
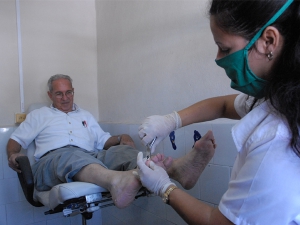 Unless diabetes is properly managed, it can lead to peripheral artery disease, which occurs when a person's blood vessels narrow, which reduces blood flow to their legs and feet. Reduced blood flow can slow wound healing. Therefore, if any cuts or grazes become infected, this infection can spread to surrounding tissue and even bones. Poor blood flow can also cause nerve damage, which may prevent a person from feeling pain. Diabetic foot ulcer is a principal diabetic complication. Diabetic foot occurs when ulcers develop from small cuts, putting sufferers at risk of amputation. It affects up to one in 10 diabetes patients. Diabetic foot is caused by high glucose levels over a prolonged period of time leading to nerve damage or loss of circulation to the body's extremities. This can cause feet to become numb. People with diabetes should frequently check their feet for signs of damage, including cuts, swelling, hardening skin and discolouration. Unfortunately, 84% of lower-limb amputations are an effect of so-called diabetic foot, chronic foot ulcers suffered by 15 to 20 percent of diabetes patients at some point in their lives. Ten to 25 percent of these patients will end up having some kind of amputation. It could be said that every 30 seconds, a diabetes patient of either sex is being amputated in a health center somewhere in the world. About 50 percent of these patients undergo a second amputation on their other lower limb. After a major amputation, fewer than 50 percent of amputees survive for more than five years.
Unless diabetes is properly managed, it can lead to peripheral artery disease, which occurs when a person's blood vessels narrow, which reduces blood flow to their legs and feet. Reduced blood flow can slow wound healing. Therefore, if any cuts or grazes become infected, this infection can spread to surrounding tissue and even bones. Poor blood flow can also cause nerve damage, which may prevent a person from feeling pain. Diabetic foot ulcer is a principal diabetic complication. Diabetic foot occurs when ulcers develop from small cuts, putting sufferers at risk of amputation. It affects up to one in 10 diabetes patients. Diabetic foot is caused by high glucose levels over a prolonged period of time leading to nerve damage or loss of circulation to the body's extremities. This can cause feet to become numb. People with diabetes should frequently check their feet for signs of damage, including cuts, swelling, hardening skin and discolouration. Unfortunately, 84% of lower-limb amputations are an effect of so-called diabetic foot, chronic foot ulcers suffered by 15 to 20 percent of diabetes patients at some point in their lives. Ten to 25 percent of these patients will end up having some kind of amputation. It could be said that every 30 seconds, a diabetes patient of either sex is being amputated in a health center somewhere in the world. About 50 percent of these patients undergo a second amputation on their other lower limb. After a major amputation, fewer than 50 percent of amputees survive for more than five years.
After a foot ulcer has formed, it will not heal as long as weight-bearing on the area continues. Unless your foot ulcer is infected, your doctor may put a cast on your leg to help the ulcer heal. Keeping your weight off your injured foot is very important. Even when you are at home, be careful to stay off that foot. Cushioned shoes, orthotic inserts, support with a cane or crutches, and - in extreme cases - a wheelchair and bed rest may be used to reduce weight and pressure on the feet. Foot infections need to be treated with antibiotics.
Diabetic Foot Treatment in Cuba
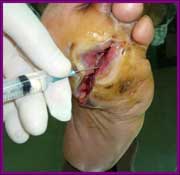 It has been shown that diabetic patients have decreased growth factor concentrations in their tissues, particularly epidermal growth factor. Growth factor shortage impairs wound healing, which leads to chronic nonhealing wounds and sometimes eventual amputation. Ischemic diabetic foot ulcer is the most difficult to treat and confers the highest amputation risk. Injecting epidermal growth factor deep into the wound bottom and contours encourages a more effective pharmacodynamic response in terms of granulation tissue growth and wound closure. Epidermal growth factor injected into the ulcer matrix may also result in association with extracellular matrix proteins, thus enhancing cell proliferation and migration.
It has been shown that diabetic patients have decreased growth factor concentrations in their tissues, particularly epidermal growth factor. Growth factor shortage impairs wound healing, which leads to chronic nonhealing wounds and sometimes eventual amputation. Ischemic diabetic foot ulcer is the most difficult to treat and confers the highest amputation risk. Injecting epidermal growth factor deep into the wound bottom and contours encourages a more effective pharmacodynamic response in terms of granulation tissue growth and wound closure. Epidermal growth factor injected into the ulcer matrix may also result in association with extracellular matrix proteins, thus enhancing cell proliferation and migration.
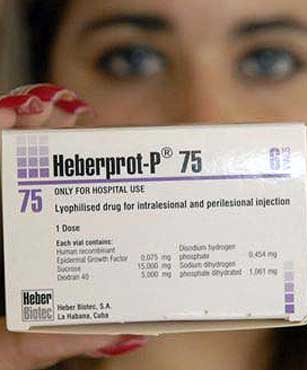
Heberprot-P, a revolutionary treatment to avoid amputation
 Heberprot-P is a drug for stimulating and sustaining scar formation for chronic ulcers of all types on the lower extremities of diabetic patients. It's a new injectable medicine developed by eminent Cuban scientists at the national Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology Center (CIGB), together with highly qualified professionals of the National Institute of Angiology and Vascular Surgery.
Heberprot-P is a drug for stimulating and sustaining scar formation for chronic ulcers of all types on the lower extremities of diabetic patients. It's a new injectable medicine developed by eminent Cuban scientists at the national Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology Center (CIGB), together with highly qualified professionals of the National Institute of Angiology and Vascular Surgery.
The use of the medication Heberprot-P with some 290,000 patients, in twenty countries, has demonstrated the possibility of ensuring the healing of open wounds, ischemic ulcers, and those caused by diabetic foot disease, increasing the formation of granulation tissue, and thus reducing the need for amputation.
The medicine contains as its active ingredient recombinant human epidermal growth factor, a peptide of 53 amino acids that couples with a receptor to activate anabolic metabolism, promoting the synthesis of amino acids and proteins, thus leading to cell division.
The product, considered unique and the first of its kind, is administered directly to the diabetic patient's ulcerated tissue, generating accelerated healing of the wound. The basic principles of its functioning were based on the research of U.S. scientist Stanley Cohen, in the 1960s, who observed the behavior of many animals which lick their wounds, applying large quantities of saliva, a pattern common among humans, as well, especially when it comes to cuts or burns on our fingers.
Beginning in the 1980s, with the development of genetic engineering, it became possible for scientists to move genes from an initial host cell to another which was easier to manipulate, principally in microbial fermenters like bacteria and yeasts, developing rapid, effective, sophisticated biotechnological procedures. These bacteria and yeasts can fabricate complex molecules of great therapeutic value at an attractive cost, and within a very brief time period.
Cuba became involved in the cloning of genes in the 1980s, as one of the world's pioneer countries in the field of biotechnology. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) was among the first molecules cloned in Cuba through genetic engineering, achieving the addition of silver sulfadiazine, used in treating burns. Produced in this way was the medication Hebermin, currently in use in burn units across Cuba's public health system, allowing for the recovery of patients with first degree burns over much of their bodies.
Currently some 458 Cuban health care centers at the primary, secondary, and tertiary levels, offer patients therapy with Heberprot-P. They have disseminated the pharmaceutical properties of the medication which promotes the growth of granulation tissue, productive in patients with ulcers that do not heal, even promoting the development of new blood vessels at the site of the open wound.
Diluted in 5ml of distilled water, the drug is injected with an appropriate hypodermic needle at a depth 0.1cm. The treatment is offered as an ambulatory service, although the patient must be bandaged and walk as little as possible. When granulation is adequate, the patient receives follow-up care from an endocrinologist during office visits with topical treatment, until the wound is fully closed.
Charcot Foot Treatment in Cuba
Charcot foot can occur in a diabetic who has neuropathy (nerve damage) in the foot that impairs the ability to feel pain. Charot foot typically occurs following a minor injury, such as a sprain or stress fracture. Because the patient doesn't feel the injury, he or she continues to walk, making the injury worse. Bones fracture, joints collapse and the foot becomes deformed. The patient walks on the side of the foot and develops pressure sores. Bones can become infected.
Both traditional surgical techniques, in which bones are held in place by internal plates and screws, (however it doesn't work with a subset of obese Charcot patients) and external fixators (see Orthopedic costs and prices in Cuba for more) are among Cuban treatment options.
Havana Diabetes Treatment Center
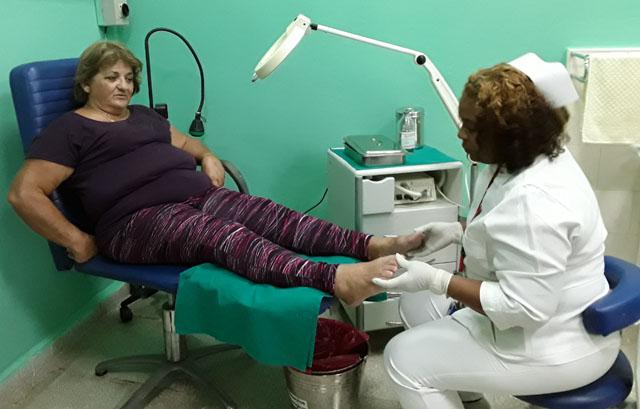 Cubans and foreigners who face living with diabetes mellitus can receive ambulatory attention, including educational information about the disease, at Havana Diabetes Treatment Center, where patients from abroad and their family members are also served. At the Center treatments are adjusted, updated information is provided, and self-management strategies developed, for patients to better handle the disease.
Cubans and foreigners who face living with diabetes mellitus can receive ambulatory attention, including educational information about the disease, at Havana Diabetes Treatment Center, where patients from abroad and their family members are also served. At the Center treatments are adjusted, updated information is provided, and self-management strategies developed, for patients to better handle the disease.
The Diabetic Treatment Center is affiliated with National Endocrinology Institute, and its principal function is education related to diabetes. During the daily ambulatory sessions, a work schedule has been established based on experience gained since 1972, when the institution was founded. Laboratory analyses are conducted to identify comorbidities and study possible complications, on the basis of individualized strategies. At all times, patients receive educational talks as they rotate through evaluative consultations with specialists, and in the afternoon hours, lectures are given on the symptoms of diabetes, foot care, nutritional habits, complications, and associated diseases, the use of medications, and other issues of interest. By the end of the week, every patient has a detailed clinical history recorded, and leaves with precise advice to better manage their disease, including lifestyle changes that improve quality of life through a more appropriate diet, in accordance with their weight and height, with specific quantities of food at the right times.
In fact, one of the special consultations offered by the institution addresses the reproductive risks faced by women with diabetes, during which young women often seek to speak with a doctor about the best time for a pregnancy. This allows steps to be taken to address risk factors to avoid fetal, neonatal, or maternal deaths, and ensure a favorable outcome for pregnant women with diabetes. Ophthalmologists are also among the most important specialists at the institution. Ophtalmologists assess the diabetic patients and insist on their learning about the disease. They check their retinas to determine if any sign of diabetic retinopathy exists, one of the disease's complications that can cause irreversible blindness.
Cuban Diabetes Control Programs
Cuba possesses strong experience in attention of diabetic people with emphasis in childhood endocrinology illnesses, obesity and Metabolic Syndrome; Disorders in Sexual Development; Reproductive Risk Factors in Diabetes and Infertility in men and women with diabetes.
Model Diabetes Mellitus Treatment Program in Cuba
The Diabetes Mellitus is one of the most frequent illnesses in the world. It is of chronic character and its inadequate handling drives to serious affectations of organs and systems that are vital to support a useful and productive life. Once controlled and with your help it will allow you to realize your daily activities and to avoid risks that could lead you to other chronic not transmissible illnesses that could bring about serious avoidable complications.
- Specialized Attention of Internal Medicine
- 10 Nights of Hospitalization
(Hospitalization in private room, air-conditioned, medical assistance and specialized nursing, programmed investigations and polyphysical therapy).
- Medical Interconsultation with Endocrinology
- Medical Interconsultation with Ophthalomology
- Investigations:
- Electrocardiogram
- Glicosilated haemoglobin
- Radiography of Thorax
- Diagnostic Ultrasound of top abdomen
- Complete Haemogram
- Uric acid
- Creatinine
- Glycemic (6)
- Total Lipids
- Urea
- Midstream clean cash
- Microalbuminuria
- Insulinemia
- Motor and sensorial neuroconduction of 4 members
The expenses corresponding to the companion are not included in this program, the person will pay $40.00 CUC daily and it will include: accommodation and meals.
This program does not include the transfer.
PRICE: $4256.00 CUC.
